How to Become a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt: Expert Guide
Becoming a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt involves training in process improvement. It requires mastering techniques to enhance quality and efficiency.
Lean Six Sigma Black Belts play a crucial role in organizations. They lead projects aimed at reducing waste and improving processes. This certification opens doors to new career opportunities and growth. It combines Lean principles, focusing on efficiency, with Six Sigma, which targets quality control.
As a Black Belt, you analyze data to solve problems and implement changes. The journey to becoming one involves rigorous training and examination. It equips you with skills to make impactful decisions. This path is ideal for those who enjoy data-driven challenges and leadership roles. Ready to elevate your career? Embark on this journey to gain expertise in a valuable field.

Introduction To Lean Six Sigma
Achieving a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt represents a significant milestone in the journey of Operational Excellence. It demands dedication, rigorous Lean Six Sigma Training, and mastery of Six Sigma Tools. Black Belt Certification is not just a credential; it signifies a commitment to Continuous Improvement and Quality Management. This introduction explores the transformative power of Lean Six Sigma and its role in advancing professional capabilities.
What Is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology designed to enhance business processes. It combines Lean principles, which focus on eliminating waste, with Six Sigma techniques that aim to reduce variability. Together, they promote Process Improvement and efficiency. Key elements include:
- Dmaic Methodology: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control – a structured approach to problem-solving.
- Statistical Analysis: Utilization of data to inform decision-making and reduce defects.
- Project Management: Effective organization and execution of improvement projects.
Lean Six Sigma is applied across various industries, from manufacturing to healthcare. It helps businesses achieve Operational Excellence by streamlining operations and improving product quality. Consider the table below illustrating key differences:
| Lean Principles | Six Sigma Principles |
|---|---|
| Focus on waste reduction | Focus on defect reduction |
| Improves flow and speed | Improves accuracy and precision |
Benefits Of Certification
Obtaining a Black Belt Certification offers numerous advantages. It opens doors to leadership roles and enhances career prospects. Certified professionals are recognized for their expertise in Quality Management and Process Improvement. Benefits include:
- Career Advancement: Opportunities for roles in Project Management and leadership.
- Skill Development: Mastery of Six Sigma Tools and Statistical Analysis.
- Increased Salary Potential: Certified individuals often command higher salaries.
A study shows certified professionals earn 10-15% more than their non-certified peers. The certification demonstrates a commitment to Continuous Improvement and the ability to drive Operational Excellence. It is a valuable asset for anyone seeking to enhance their professional journey.
Key Principles Of Lean Six Sigma
Understanding the key principles of Lean Six Sigma is crucial for those pursuing a Black Belt certification. This methodology focuses on Continuous Improvement and Waste Reduction to enhance business processes. Lean Six Sigma combines tools from both Lean and Six Sigma to improve efficiency and quality. Its core principles, known as the DMAIC methodology—Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control—form the backbone of process improvement and quality management.
Define
In the Define phase, clarity is key. Start by identifying the problem you need to solve. This step involves setting clear objectives and understanding the scope of the project. A well-defined problem statement guides the entire process. During Black Belt Training, you’ll learn to:
- Identify customer needs and expectations.
- Define project goals aligned with business objectives.
- Establish a project charter to outline scope and responsibilities.
This phase sets the foundation for the entire Lean Six Sigma project. Defining the project correctly ensures everyone is on the same page, enhancing Project Management efficiency.
Measure
The Measure phase focuses on quantifying the problem. Here, data collection is critical. Reliable data helps assess current process performance. Key tasks include:
- Identifying Performance Metrics relevant to the project.
- Collecting data to understand baseline performance.
- Using Statistical Analysis to validate measurement systems.
Successful measurement provides a clear picture of current operations. This clarity is essential for effective Process Improvement and Waste Reduction. Accurate data collection lays the groundwork for informed decision-making.
Analyze
Analysis turns data into insights. The Analyze phase seeks to identify the root cause of problems. During this phase, you will:
- Use Statistical Analysis tools to interpret data.
- Identify patterns and relationships in the data.
- Pinpoint the causes of defects and inefficiencies.
Understanding the root cause is critical for effective solutions. This phase helps ensure that improvements are based on facts, not assumptions. Analyzing data thoroughly aids in targeted Process Improvement.
Improve
The Improve phase focuses on developing solutions. Here, creativity and analysis combine to enhance processes. Key activities include:
- Brainstorming potential solutions to address root causes.
- Testing solutions on a small scale to assess their impact.
- Implementing solutions that demonstrate positive changes.
This phase emphasizes Continuous Improvement, ensuring solutions lead to significant enhancements. The goal is to implement changes that deliver sustainable improvements in quality and efficiency.
Control
The Control phase ensures that improvements are maintained. This phase involves setting up systems to monitor and sustain changes. Key actions include:
- Developing control plans to track process performance.
- Implementing standard operating procedures for consistency.
- Using Performance Metrics to ensure ongoing quality.
Effective control prevents backsliding, ensuring that gains are permanent. This phase is crucial for maintaining the benefits of Lean Six Sigma projects. Control mechanisms safeguard the improvements achieved through the DMAIC methodology.
Prerequisites For Black Belt
Embarking on the journey to become a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt is a rewarding pursuit for those passionate about Operational Excellence and Continuous Improvement. Achieving this level of expertise means mastering the Six Sigma Methodology and the DMAIC Framework. Before starting Black Belt Training, it’s vital to understand the prerequisites that will ensure your readiness for this rigorous certification. From educational qualifications to practical experience, these foundational elements prepare you for the challenges of Project Management and Quality Management inherent in Black Belt roles.
Educational Requirements
To pursue Lean Six Sigma Certification at the Black Belt level, certain educational prerequisites should be met. While there is no strict requirement for a specific degree, having a background in fields related to Process Improvement or Statistical Analysis can be beneficial. Here are key aspects to consider:
- A bachelor’s degree is often preferred. It provides foundational knowledge that supports the complex concepts of Six Sigma Methodology.
- Courses in mathematics, engineering, or business administration enhance understanding of the statistical tools used in Six Sigma.
- Training in Quality Management or Project Management adds value by equipping candidates with the skills needed for effective leadership.
Educational preparation also involves gaining familiarity with the DMAIC Framework. You can achieve this through:
- Online courses and workshops that offer basic and advanced Lean Six Sigma concepts.
- Textbooks and literature focusing on Operational Excellence and Continuous Improvement strategies.
While a formal education lays the groundwork, it is the application of these principles that truly prepares you for Black Belt Training.
Experience Needed
Experience plays a crucial role in becoming a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt. Practical exposure to real-world scenarios sharpens your ability to implement Process Improvement effectively. Ideal candidates typically have:
- Several years of experience in roles that emphasize Quality Management and Operational Excellence.
- Hands-on involvement in projects that utilize the Six Sigma Methodology, particularly the DMAIC Framework.
- Experience in leading or supporting Project Management initiatives aimed at Continuous Improvement.
Gaining experience can also involve:
| Type of Experience | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Improvement Projects | Working on projects to refine and optimize business processes. |
| Statistical Analysis | Using data-driven techniques to identify and solve problems. |
| Leadership Roles | Leading teams and projects to drive quality improvements. |
Engaging in these experiences not only builds competence but also confidence in applying Lean Six Sigma principles. This practical know-how is essential for the challenges faced during Black Belt Training.
Choosing A Certification Program
Choosing the right certification program is a crucial step for anyone aspiring to become a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt. This certification represents a high level of expertise in Operational Excellence and Continuous Improvement. Understanding how to select a program that aligns with your career goals and learning style can significantly enhance your knowledge of Six Sigma Methodologies, Problem-Solving Techniques, and Quality Management.
Accredited Institutions
Picking an accredited institution ensures that your Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Training is recognized globally. Accredited institutions provide structured courses that cover Project Management, Statistical Analysis, and Process Improvement. Here are key factors to consider:
- Reputation: Choose institutions with a solid reputation in Lean Six Sigma Certification.
- Accreditation: Verify the institution’s accreditation status with recognized bodies.
- Curriculum: Ensure the curriculum includes comprehensive coverage of Six Sigma Methodologies.
- Instructor Expertise: Look for instructors with real-world experience in Operational Excellence.
| Institution | Accreditation | Reputation |
|---|---|---|
| Institution A | ISO Certified | Highly Rated |
| Institution B | ASQ Accredited | Well Known |
Course Formats
The format of Black Belt Training courses varies widely. Understanding these options helps you select a program that fits your schedule and learning style. Course formats can include:
- Online: Ideal for those who need flexible scheduling.
- In-Person: Provides hands-on experience in Problem-Solving Techniques.
- Hybrid: Combines online and in-person elements for a balanced approach.
Online courses offer convenience and accessibility. They often include interactive modules on Quality Management and Process Improvement. In-person courses facilitate direct interaction with instructors, enhancing your understanding of Statistical Analysis and Project Management. Hybrid courses blend both methods, offering flexibility while maintaining a high level of engagement. Consider your personal schedule, learning preferences, and career goals when choosing the best course format.
Preparing For The Exam
Embarking on the journey to become a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt is both exciting and challenging. To succeed, one must focus on the crucial step of preparing for the exam. This preparation ensures you are well-versed in Continuous Improvement and the essential Quality Control Techniques. As you gear up for the test, it’s important to gather the right study materials and take practice tests to sharpen your skills. Below, we delve into how these elements can aid your path to Lean Six Sigma Certification.
Study Materials
Choosing the right study materials is key to mastering the Six Sigma Principles and other vital concepts. Quality Management and Project Management are integral parts of the Black Belt Training. Here are some essential resources:
- Books: Consider titles like “The Six Sigma Handbook” and “Lean Six Sigma for Dummies.” These books offer insights into Process Improvement and Statistical Analysis.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Udemy provide comprehensive courses on the Dmaic Methodology.
- Webinars and Workshops: Engage in sessions that focus on Quality Control Techniques and Continuous Improvement.
A well-rounded study plan includes a mix of these materials. This approach ensures you grasp both theoretical and practical aspects of Lean Six Sigma Certification.
| Resource Type | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Books | The Six Sigma Handbook, Lean Six Sigma for Dummies |
| Online Courses | Coursera, Udemy |
| Webinars | Focused on Quality Management and Process Improvement |
Practice Tests
Practice tests are a critical part of exam preparation. They help solidify your understanding of Black Belt Training concepts. Regularly taking these tests can identify areas needing improvement in your knowledge of Quality Management and the Dmaic Methodology. Here’s how to effectively use practice tests:
- Simulate Exam Conditions: Time yourself. Create an environment similar to actual exam settings.
- Analyze Results: After each test, review your answers. Focus on incorrect responses to understand mistakes.
- Track Progress: Keep a record of your scores. This tracking highlights improvements in understanding Statistical Analysis and Process Improvement.
Practice tests not only prepare you for the type of questions but also build confidence. This boosts your readiness for the Lean Six Sigma Certification exam.
Project Requirements
Becoming a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt involves a deep dive into complex problem-solving techniques, honing skills in project management and quality management. A crucial part of this journey is understanding the project requirements. Projects are the backbone of Black Belt training, providing real-world challenges and opportunities to apply Lean Six Sigma methodologies like DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control). These projects focus on operational excellence and continuous improvement, ensuring that each candidate gains hands-on experience in statistical analysis and process improvement. Understanding the project requirements is essential for effective training and successful Lean Six Sigma certification.
Real-world Application
Real-world application is a cornerstone of Lean Six Sigma Black Belt training. Projects undertaken during this phase are not theoretical exercises. They are real challenges faced by businesses. Tackling these projects helps candidates develop practical skills in problem-solving techniques and quality management. These projects often involve:
- Operational Excellence: Streamlining processes to reduce waste and improve efficiency.
- Continuous Improvement: Implementing incremental changes that lead to significant improvements.
- Statistical Analysis: Using data to make informed decisions and drive change.
Real-world projects require candidates to apply DMAIC methodology, ensuring a structured approach to process improvement. This methodology involves:
- Define: Identifying the problem and project scope.
- Measure: Collecting data to quantify the issue.
- Analyze: Examining data to find root causes.
- Improve: Developing solutions to address root causes.
- Control: Implementing controls to sustain improvements.
Through these projects, Black Belt candidates learn to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations, preparing them for leadership roles in process improvement and quality management.
Project Selection Criteria
Choosing the right project is crucial for effective Black Belt training. Projects must align with specific criteria to ensure they provide valuable learning experiences. Key criteria include:
- Scope: Projects should have a clear and manageable scope. Overly complex projects can hinder learning.
- Impact: Projects should have the potential for significant impact on operational excellence and continuous improvement.
- Feasibility: Projects must be feasible within the given timeframe and resources.
Projects should involve challenges in quality management and process improvement. Statistical analysis should be integral to the project, allowing candidates to apply their skills effectively. A well-chosen project provides a comprehensive learning experience, enhancing the candidate’s ability to implement Lean Six Sigma methodologies. Projects should also support the organization’s strategic goals, ensuring alignment with broader objectives. Black Belt candidates must select projects that not only challenge their abilities but also contribute to the organization’s success. A table can help in evaluating potential projects:
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Scope | Defined and manageable |
| Impact | Potential for significant improvement |
| Feasibility | Achievable within resources |
| Strategic Alignment | Supports organizational goals |
By selecting projects based on these criteria, candidates ensure they gain valuable skills in project management and Lean Six Sigma certification.
Exam Day Tips
Preparing for the Lean Six Sigma Black Belt exam can be a daunting experience. After months of Black Belt Training, studying the Six Sigma Principles, and mastering Problem-Solving Techniques, exam day can feel overwhelming. To assist you in this crucial phase, consider some practical Exam Day Tips. These strategies will help you remain calm, focused, and ready to tackle the challenge. Let’s dive into what you can expect and how to manage exam anxiety effectively.
What To Expect
On exam day, it’s essential to know what lies ahead. This understanding helps reduce stress and keeps you focused on the task. The Lean Six Sigma Black Belt exam typically assesses your knowledge of Continuous Improvement, Process Improvement, and Quality Management. You’ll encounter questions on Project Management and Statistical Analysis, testing your grasp of these crucial subjects.
- Multiple-choice questions: Expect a series of questions that evaluate your understanding of the Dmaic Methodology and other Six Sigma Principles.
- Time constraints: The exam is timed. Ensure you manage your time wisely, allocating adequate minutes to each question.
- Calculator usage: Familiarize yourself with permitted calculators. They are vital for solving Statistical Analysis problems.
- Exam format: The exam may be computer-based or paper-based, depending on the certifying body.
Understanding the structure can make a significant difference. Here’s a simple table to help you visualize the exam components:
| Component | Details |
|---|---|
| Question Type | Multiple-choice |
| Duration | Approximately 4 hours |
| Topics Covered | Quality Management, Project Management, Process Improvement |
Prepare thoroughly. You’ll feel more confident and ready to succeed.
Managing Exam Anxiety
Managing exam anxiety is crucial for optimal performance. Feeling nervous is normal, but excessive anxiety can hinder your abilities. Here are some strategies to stay calm and focused:
- Practice relaxation techniques: Deep breathing and meditation can help ease tension. Take a few minutes to calm your mind before the exam.
- Stay organized: Gather all necessary materials the night before. This preparation prevents last-minute panic.
- Positive visualization: Visualize yourself succeeding. Imagine walking out of the exam room with confidence.
- Healthy habits: Ensure a good night’s sleep and a nutritious meal. Both improve concentration and stamina.
- Time management: Practice answering questions within a set time. This strategy builds confidence and efficiency.
Remember, anxiety is a part of the process. Use it to fuel your determination and focus on demonstrating your knowledge of Lean Six Sigma Certification and Continuous Improvement. Stay positive and believe in your preparation. You’ve got this!
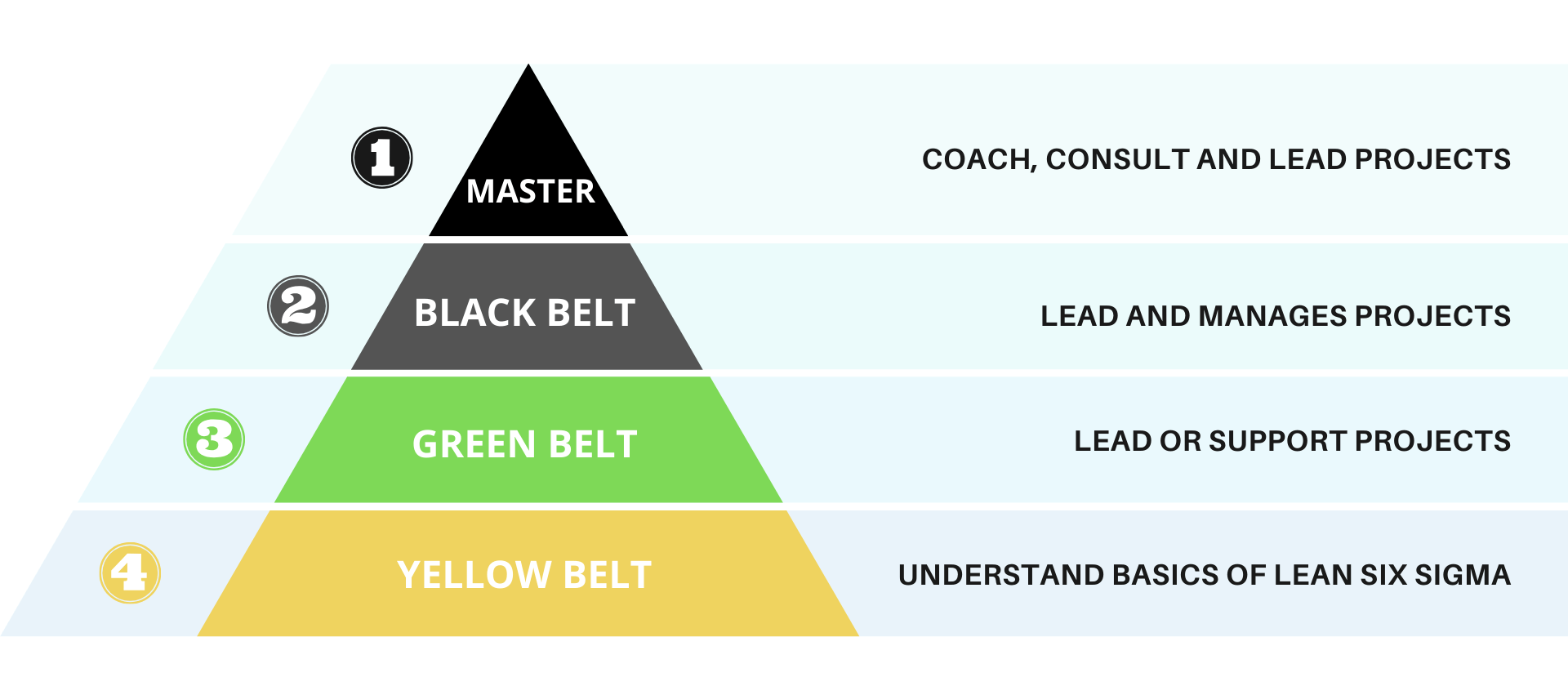
Post-certification Opportunities
After earning your Lean Six Sigma Black Belt certification, a world of opportunities opens up. This certification signifies expertise in improving processes and solving complex problems. It shows your commitment to Operational Excellence and Quality Management. What comes next? Let’s explore the paths available to you after certification.
Career Pathways
With a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt, you can pursue various career pathways. This certification is highly respected in many industries. Here are some common roles:
- Process Improvement Manager: Oversee projects aimed at boosting efficiency and productivity.
- Quality Assurance Director: Ensure products and services meet quality standards.
- Operational Excellence Consultant: Advise companies on achieving peak performance.
- Project Manager: Lead teams to complete projects using Dmaic Methodology.
These roles often require strong Leadership Skills and expertise in Six Sigma Tools. Let’s look at how these roles can impact your career:
| Role | Impact |
|---|---|
| Process Improvement Manager | Streamlines operations, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. |
| Quality Assurance Director | Maintains high standards, enhancing customer satisfaction. |
| Operational Excellence Consultant | Drives company growth through strategic improvements. |
| Project Manager | Ensures projects are on time and within budget. |
Continued Learning
Even after achieving your Black Belt, continued learning is crucial. The field of Process Improvement is always evolving. Staying updated ensures you remain competitive. Here are ways to continue learning:
- Advanced Certifications: Consider pursuing a Master Black Belt for deeper expertise.
- Workshops and Seminars: Attend events focused on the latest in Data Analysis and Six Sigma Tools.
- Online Courses: Many platforms offer courses in Black Belt Training and Project Management.
- Professional Networks: Join groups focused on Lean Six Sigma Certification.
Each of these avenues provides new insights and skills. They help you stay ahead in Quality Management and Operational Excellence. Remember, learning is a lifelong journey. The more you know, the better you can lead and innovate.

Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does It Take To Get A Lean Six Sigma Black Belt?
Earning a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt typically takes 1 to 3 months. This includes training and project completion. Course duration varies based on program intensity and learning pace. Online and in-person options are available, offering flexibility in scheduling. Successful completion requires dedication and commitment to mastering advanced quality management techniques.
How To Become A Black Belt In Six Sigma?
To become a Six Sigma Black Belt, complete a training program from a reputable provider. Gain hands-on experience by leading projects. Pass the certification exam. Develop skills in project management, leadership, and data analysis. Stay updated with industry trends and continuous improvement techniques.
Can I Go Straight To Lean Six Sigma Black Belt?
Yes, you can go straight to Lean Six Sigma Black Belt. Prior experience or certification is beneficial but not mandatory. Some training programs offer direct Black Belt courses, ensuring you grasp advanced concepts and techniques. Always check specific program requirements to ensure eligibility.
Can I Get Six Sigma Black Belt Without Experience?
Yes, you can earn a Six Sigma Black Belt without experience. Many training programs welcome beginners. Focus on learning methodologies and tools. Gaining practical experience during the course is beneficial. Certification can boost your career by showcasing your commitment to process improvement.
Conclusion
Becoming a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt takes dedication and learning. You gain skills that improve processes and solve problems. This certification boosts your career and opens new paths. You lead projects with confidence and make impactful changes. Courses, practice, and exams are part of the journey.
Stay committed and focused. Keep learning and applying what you learn. Each step brings you closer to your goal. Achieve success with hard work and perseverance. Your future in Lean Six Sigma starts now. Embrace the challenge and enjoy the rewards.
Make a difference with your new skills.















.jpg)






