How to Become an Ambulance Care Assistant: Expert Tips
You’ve always been drawn to helping others, and the idea of making a real difference in people’s lives excites you. Becoming an Ambulance Care Assistant could be your path to achieving just that.
Imagine being the first comforting presence for someone in need, providing essential support during emergencies, and working alongside skilled medical professionals. It’s a role filled with purpose and impact. You’ll discover the steps to turn your passion into a rewarding career as an Ambulance Care Assistant.
We’ll guide you through the qualifications you need, the skills to develop, and what to expect on the job. You’ll learn how to become a vital part of the healthcare system and why this career choice could be the perfect fit for you. Are you ready to explore how you can make a difference every day? Read on and find out how you can start your journey today.
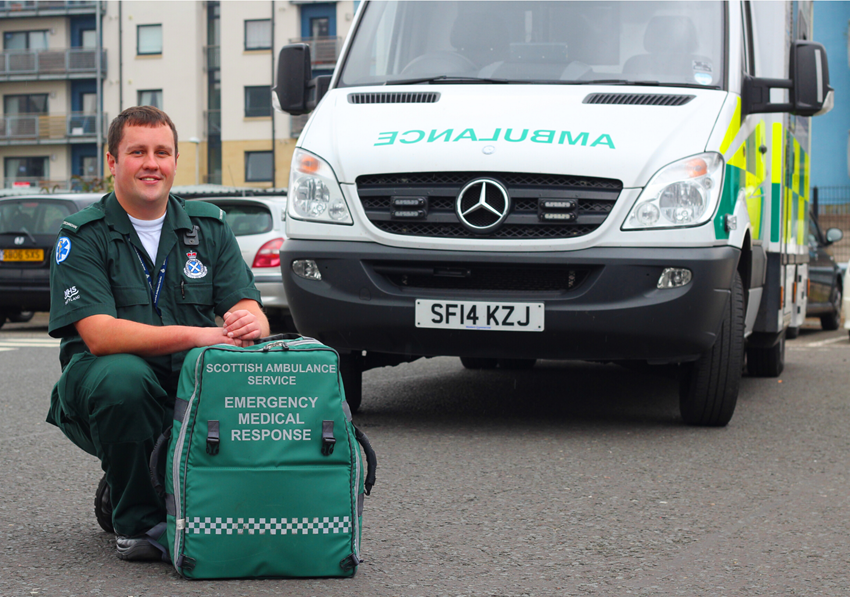
Role Of An Ambulance Care Assistant
An ambulance care assistant supports paramedics and provides patient care during transport. Training involves first aid certification, basic life support, and communication skills. Completing a healthcare course and gaining practical experience enhances your chances of success in this vital role.
The role of an Ambulance Care Assistant (ACA) is crucial in the healthcare sector. These professionals provide vital support to paramedics and ensure patients receive care and comfort during transportation. If you’re considering a career as an ACA, understanding the responsibilities and expectations is essential.
Understanding Daily Responsibilities
ACAs help transport patients safely to and from medical facilities. They assist with lifting and moving patients, ensuring their comfort throughout the journey. Your day will often involve driving the ambulance, so a clean driving record and good navigation skills are important.
Providing Emotional Support
Interacting with patients is a significant part of the job. Many patients may be anxious or in distress, and your calm demeanor can make a huge difference. Offering reassurance and a listening ear can help ease their concerns.
Assisting Medical Professionals
You will work closely with paramedics and other healthcare staff. This includes preparing equipment and supporting them during medical procedures. Being attentive and responsive to their needs is key to effective teamwork.
Maintaining Equipment And Vehicles
Regular checks of medical equipment and the ambulance are part of your role. Ensuring everything is in working order helps prevent delays in emergencies. Attention to detail in these tasks ensures patient safety and care efficiency.
Developing Key Skills
Strong communication skills are essential for interacting with patients and colleagues. You will also need good physical stamina due to the demands of lifting patients and equipment. Consider if you enjoy dynamic, fast-paced environments where every day is different. Are you ready to make a meaningful impact in healthcare? The role of an ACA offers a rewarding path for those dedicated to helping others. With the right skills and mindset, you can make a difference in patients’ lives every day.

Essential Skills And Qualities
Becoming an ambulance care assistant requires a blend of key skills. These skills ensure you provide the best care in emergencies. Understanding these skills and qualities is essential for success in this role. Let’s explore the core skills needed to excel as an ambulance care assistant.
Communication And Empathy
Effective communication is critical in emergency situations. You must speak clearly to patients and colleagues. Empathy helps you connect with patients on a personal level. Understanding their emotions makes a difference. It comforts them during stressful times. Being a good listener is also important. It helps in gathering accurate information quickly.
Physical Stamina And Dexterity
Physical stamina is vital for an ambulance care assistant. You often work long hours and need strength to assist patients. Dexterity is essential for handling equipment. Quick and precise movements can save lives. Maintaining fitness and flexibility is crucial for your role. It ensures you perform tasks effectively under pressure.
Problem-solving Abilities
Problem-solving skills are vital in emergencies. You need to think fast and act wisely. Assessing situations quickly helps in deciding the best action. Creativity in solutions can ease challenging scenarios. Analyzing information accurately is necessary. It leads to better decision-making in critical moments.
Educational Requirements
Becoming an ambulance care assistant requires specific educational qualifications. These qualifications ensure you are prepared for the job’s demands. They provide you with the necessary skills to offer excellent patient care. Here, we explore the fundamental educational requirements you need.
High School Diploma
A high school diploma is often the first step. This qualification ensures you have a basic understanding of essential subjects. Subjects like math and science are particularly useful. These subjects help you develop analytical and problem-solving skills. They are crucial in emergency situations.
First Aid And Cpr Certification
First Aid and CPR certification are vital for ambulance care assistants. These certifications teach life-saving techniques. They prepare you to handle emergencies effectively. You learn how to assist patients in critical conditions. This training builds your confidence and competence in the field.
Certifications are offered by various organizations. Choose a reputable source for your training. Ensure your skills are up-to-date. Continuous learning is key in healthcare professions.
Training Programs And Certifications
Thinking about becoming an Ambulance Care Assistant? You’ll need a blend of skills, compassion, and training. This role is rewarding, but getting the right training and certifications is crucial. Let’s explore what you need to know about training programs and certifications to kickstart your career.
Vocational Training Courses
Vocational training courses are an excellent starting point. These courses offer structured learning, focusing on both theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
Look for courses that include first aid, patient transport, and basic life support. These are essential for your daily responsibilities.
Some programs even offer simulation exercises, allowing you to practice real-life scenarios in a controlled environment. This experience can be invaluable.
Have you ever wondered how you would react in a high-pressure situation? These courses help you develop the confidence and skills to manage emergencies effectively.
On-the-job Training
On-the-job training is where theory meets practice. Here, you’ll learn directly from experienced professionals while working in the field.
You’ll have the opportunity to shadow seasoned ambulance care assistants. This firsthand experience is crucial for understanding the nuances of patient care.
Ask questions and absorb as much information as you can. This is your chance to learn the tricks of the trade that textbooks don’t cover.
Do you have any concerns about handling real patients? On-the-job training will equip you with the skills and confidence to care for patients with empathy and efficiency.
Remember, each day on the job is a learning experience. Embrace it and grow from it.
Gaining Practical Experience
Gaining practical experience is crucial for aspiring ambulance care assistants. It bridges the gap between theory and real-world application. Hands-on experience not only enhances skills but also boosts confidence. It’s the key to understanding the daily challenges and rewards of the role.
Volunteering Opportunities
Volunteering is a great way to gain experience. Many organizations seek volunteers for various roles. You can assist in community events or health clinics. This involvement provides real-world exposure. It helps you understand patient care dynamics. Additionally, volunteering demonstrates your commitment to the field.
Internship Programs
Internship programs offer structured learning environments. Many hospitals and ambulance services offer internships. These programs provide supervised, hands-on training. Interns work alongside experienced professionals. They learn vital skills in patient care and transport. Internships also enhance your resume and increase job prospects.
Applying For Positions
Applying for positions as an Ambulance Care Assistant requires careful preparation. You want to stand out among other candidates. Start by understanding the job role and what employers seek. This helps in tailoring your application effectively. Focus on highlighting relevant skills and experiences.
Crafting A Professional Resume
Your resume should reflect your skills and experience in healthcare. Highlight any experience in medical or emergency settings. Use bullet points for clarity. Include certifications or training relevant to the role. Keep it concise and easy to read.
Focus on your strengths. Show your ability to work under pressure. Use action verbs to describe your achievements. Employers prefer candidates who can handle stress effectively. Tailor your resume for each job application.
Interview Preparation Tips
Prepare for interviews by researching common questions. Understand the responsibilities of an Ambulance Care Assistant. Practice your answers. Be ready to discuss your experience and skills. Show your passion for helping others.
Dress professionally for the interview. This shows respect and seriousness. Arrive early to demonstrate punctuality. Maintain eye contact and a positive attitude. Be honest about your skills and experiences. Ask questions to show your interest in the role.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Embarking on a career as an Ambulance Care Assistant can be just the beginning of a fulfilling journey in the healthcare sector. As you gain experience, numerous career advancement opportunities await you. Whether you’re looking to specialize or further your education, the possibilities are vast and exciting. Let’s dive into how you can take your career to the next level.
Specialization Areas
As an Ambulance Care Assistant, you have the chance to specialize in different areas that can enhance your skillset. Consider focusing on pediatric care, where you work closely with children during emergencies. Alternatively, mental health support specialization can be rewarding, helping individuals in crisis situations.
Specializing allows you to become an expert in a niche field, making you invaluable to your team. Think about what interests you most and pursue it with dedication. Specialization often leads to more responsibilities and, potentially, higher pay.
Further Education And Training
Education is a powerful tool for career advancement. Look into courses that can expand your knowledge and skills. Many organizations offer training programs that can be completed alongside your job.
Consider enrolling in courses like advanced life support or trauma care. These programs can provide you with the expertise needed to handle more complex situations effectively. With additional training, you can take on roles with more responsibility, such as a team leader or instructor.
Are you passionate about learning? If so, pursuing further education could be your ticket to a fulfilling career. Engaging in continuous learning not only boosts your capabilities but also keeps you updated with the latest healthcare practices.
What steps will you take to advance your career? The opportunities are there for those willing to seize them.
Challenges In The Field
Navigating the path to becoming an ambulance care assistant involves overcoming various challenges. Understanding medical protocols and handling stressful situations are essential skills. Building strong communication skills helps in providing effective care and support.
Becoming an Ambulance Care Assistant is a fulfilling yet challenging journey. The role demands a balance of physical stamina and emotional resilience. You will face various challenges that test both your professional skills and personal strength.
Managing Stressful Situations
Handling emergencies is part of the job. Each call can present a new challenge, from traffic accidents to medical emergencies. You must think quickly and stay calm under pressure. Imagine responding to a multi-car crash—your ability to assess the situation swiftly and take decisive action can make all the difference. How do you handle stress? Developing coping strategies is key. Consider practicing mindfulness or engaging in regular physical exercise to maintain your mental clarity.
Dealing With Emotional Strain
Emotional strain is an inevitable part of working as an Ambulance Care Assistant. Witnessing distress and suffering can take a toll on your mental health. It’s crucial to process these experiences healthily. Remember a time when you comforted a grieving family member—such moments can be emotionally taxing, but they also offer opportunities for growth and empathy. Talking to colleagues and mental health professionals can provide support and perspective. Never underestimate the power of a supportive community to help you navigate these emotional challenges.
Expert Tips For Success
Becoming an Ambulance Care Assistant demands dedication and skill. Success in this field requires more than basic training. Understanding the nuances and embracing the journey can enhance your career. Here are expert tips to guide you.
Continuous Learning
Stay updated with medical advancements. These changes impact patient care. Regular courses can enhance your skills. Consider online platforms for flexibility. Read medical journals. They offer insights into new treatments. Attend workshops. They provide hands-on experience.
Networking And Professional Relationships
Building relationships is crucial. Connect with other professionals. They offer valuable advice. Join healthcare forums. These platforms share industry news. Attend healthcare conferences. Meet experts and learn from their experience. Collaborate with colleagues. Teamwork improves patient care.

Frequently Asked Questions
What Qualifications Are Needed For An Ambulance Care Assistant?
To become an Ambulance Care Assistant, you typically need a high school diploma. Some employers might require additional healthcare qualifications or first aid certifications. Strong communication and driving skills are also essential. On-the-job training is usually provided to help you understand the specific duties and responsibilities.
How Do I Apply For Ambulance Care Assistant Roles?
To apply, search for job openings at local hospitals or ambulance services. Prepare a well-written resume highlighting relevant skills and experiences. Include any healthcare or first aid certifications. Submit your application online or in person. Follow up with a phone call or email to express your interest.
What Skills Are Important For This Role?
Key skills for an Ambulance Care Assistant include excellent communication and empathy. You should be able to handle stressful situations calmly. Basic first aid knowledge and the ability to work as part of a team are essential. Strong driving skills are also important as you may need to transport patients.
Is Previous Experience Required For This Job?
Previous experience in a healthcare or patient care setting is beneficial but not always required. Many employers provide on-the-job training for new Ambulance Care Assistants. Demonstrating a genuine interest in healthcare and having strong interpersonal skills can compensate for lack of direct experience.
Conclusion
Becoming an ambulance care assistant is a rewarding journey. You make a difference daily. With the right training, dedication, and compassion, you can succeed. This role involves helping others in critical times. Skills grow with experience and learning. Remember, patience and empathy are key.
Start with basic requirements and build your qualifications. Stay informed about new medical practices. Network with professionals for guidance and support. Your efforts lead to a fulfilling career. Each day, you help save lives. That’s a noble calling. So, embark on this path with confidence and passion.
Your community needs you.



















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/FAW-Breville_BaristaTouch_BES880_23-CoffeeMakers-0763-Russell-Kilgore-3x2-fbbd28003fd8427e8337cf2eeba7e9b1.jpeg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/FAW-Breville_BaristaExpress_BES870XL_22-0791-Russell-Kilgore-3x2-1-2e0238f489bf4a92a01770a3bdc8daef.jpeg)